Need help? Call us:
+91 9899799757
Shopping cart (0)
Subtotal: ₹0.00
Spend ₹1,000.00 to get free shipping
Congratulations! You've got free shipping.
Pro Micro 5V 16M Mini Leonardo...
₹507.63 Original price was: ₹507.63.₹202.54Current price is: ₹202.54. Inc.GST Excl. GST: ₹202.54


Arduino Uno R3 Board with USB ...
₹1,694.07 Original price was: ₹1,694.07.₹482.20Current price is: ₹482.20. Inc.GST Excl. GST: ₹482.20
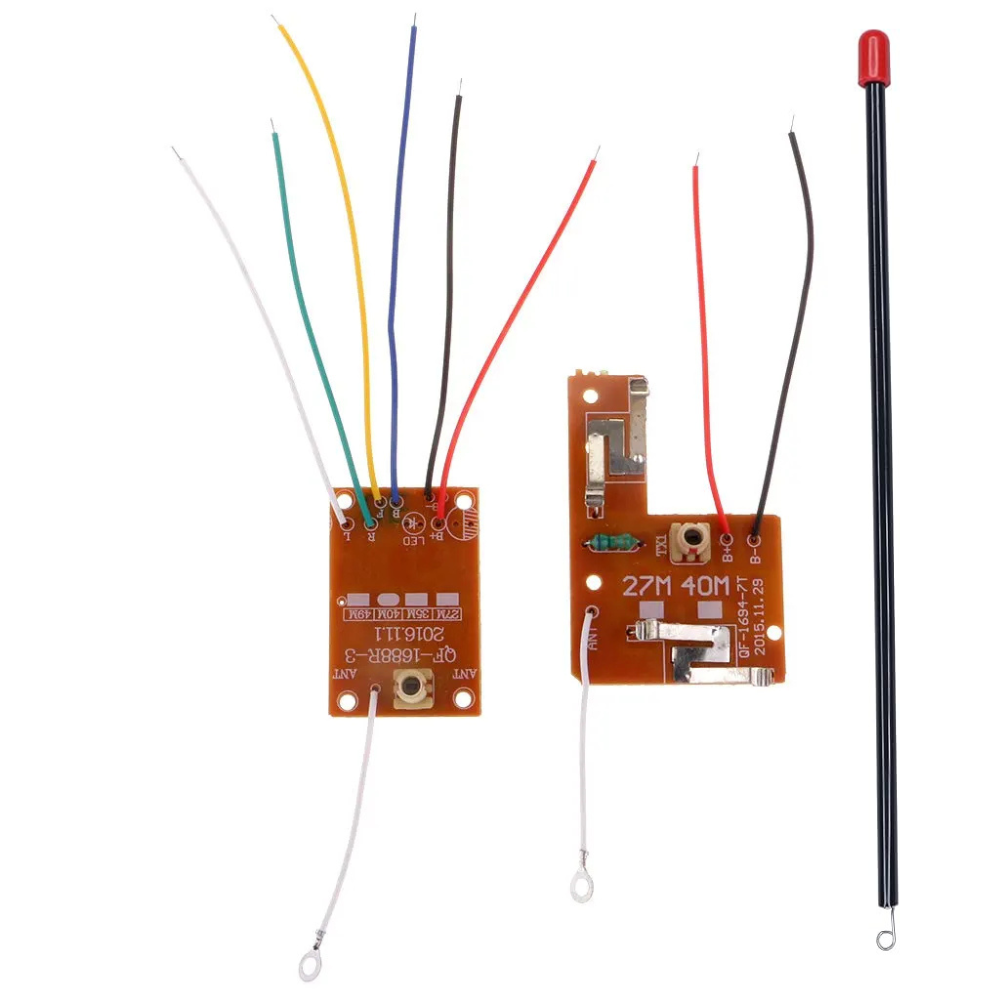
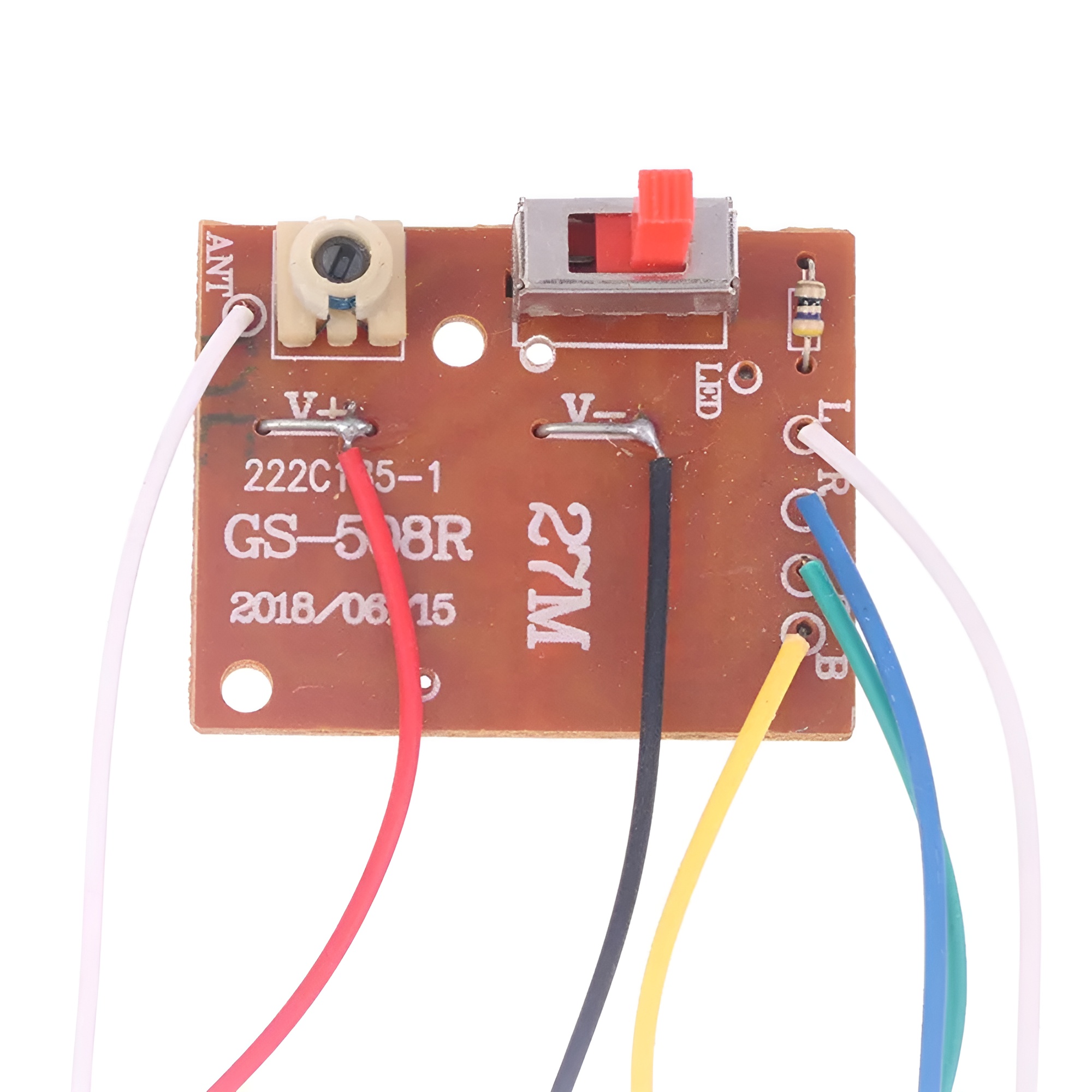
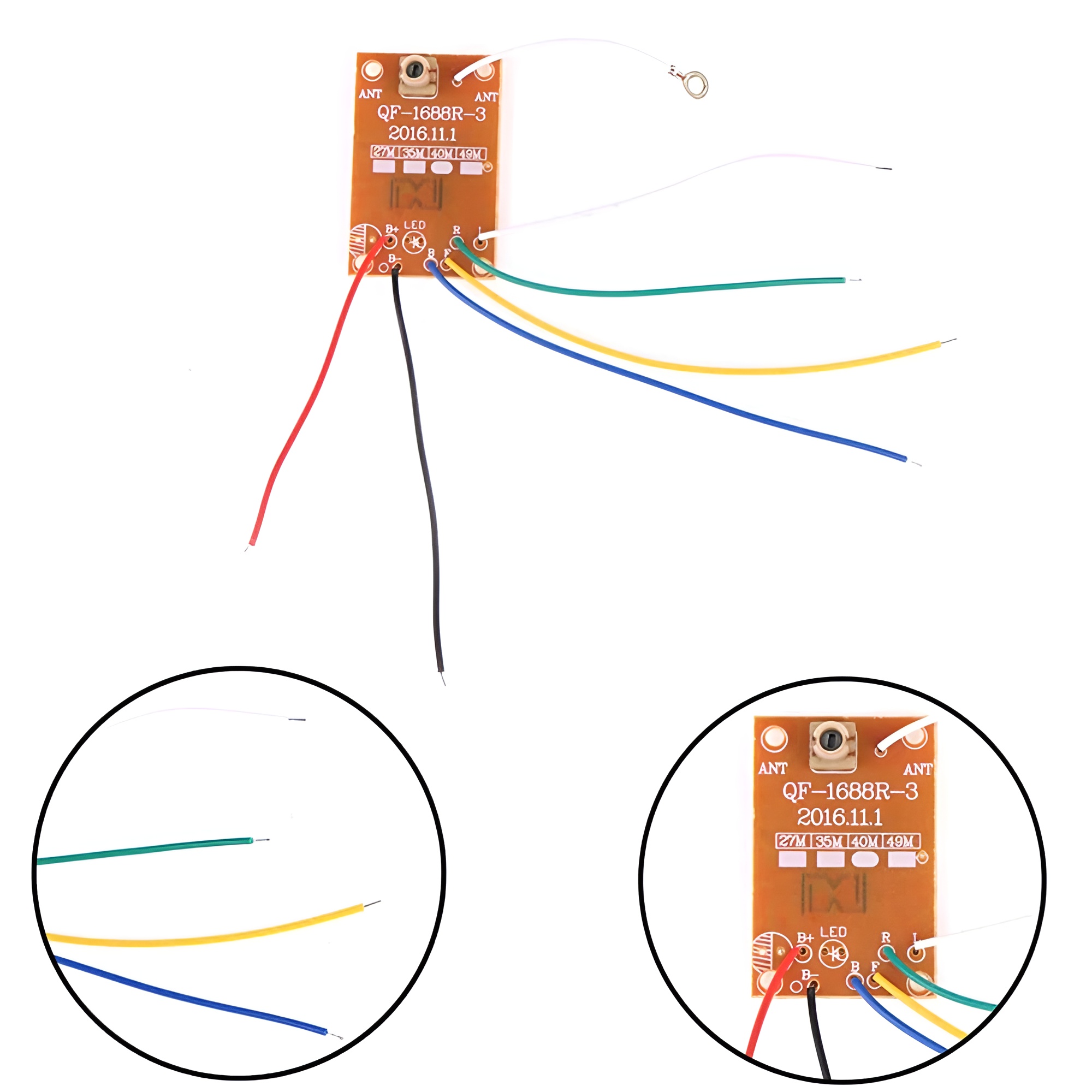
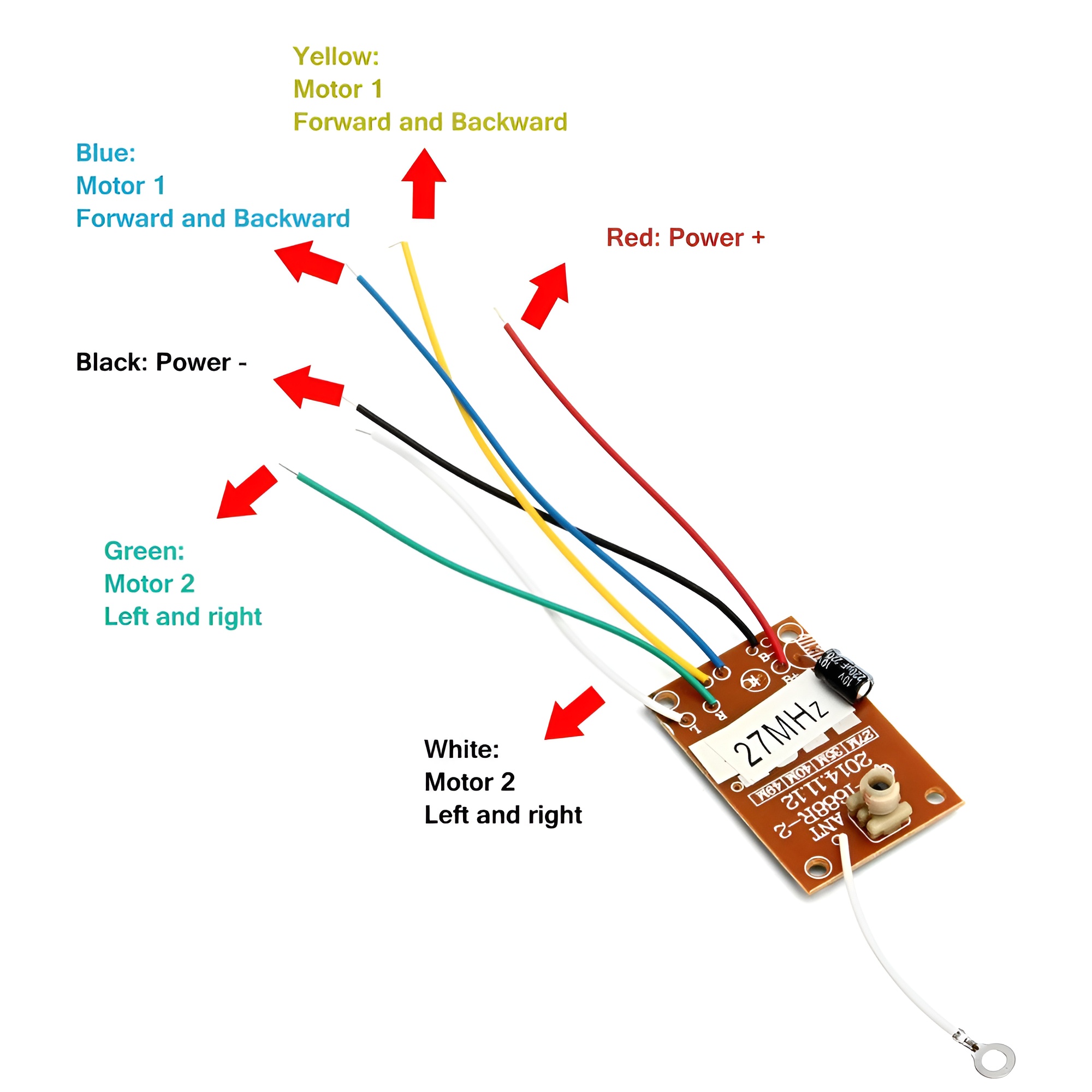
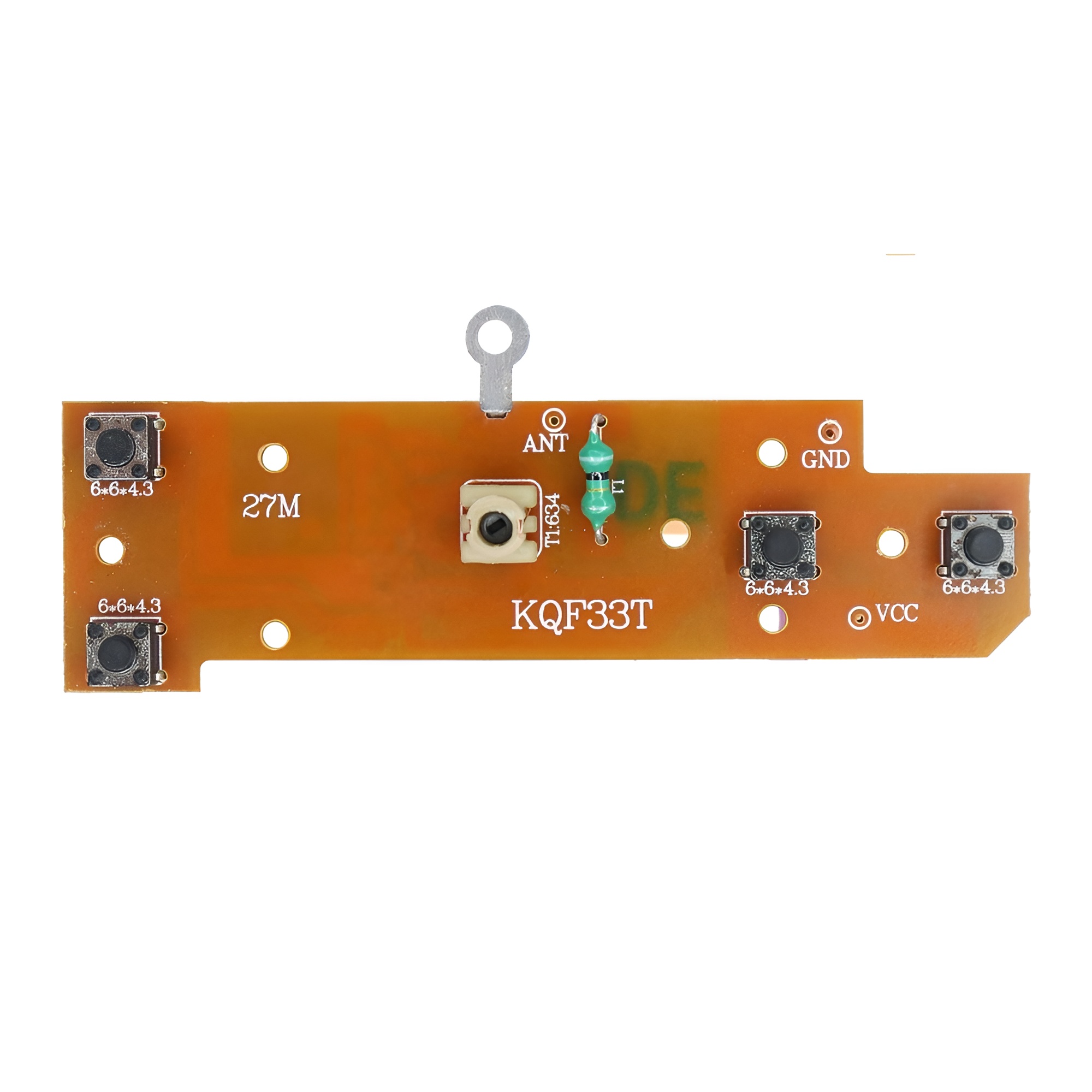
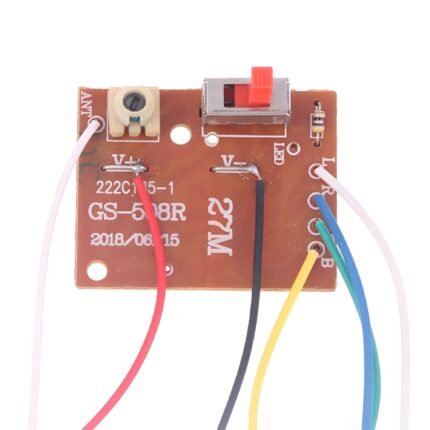
4-Channel RC Transmitter and Receiver 27MHz Circuit PCB Remote Control
Brand:
24 people are viewing this product right now
₹507.63 Original price was: ₹507.63.₹134.75Current price is: ₹134.75. Inc.GST Excl. GST: ₹134.75
Shipping calculated at checkout.
🔥 Buy More Save More!
Buy 3 items get 5% OFF
on each productBuy 6 items get 7% OFF
on each productBuy 10 items get 10% OFF
on each product
Estimated delivery:04/09/2025
SKU:
261590
Categories: CONTROLLER, ELECTRONIC COMPONENTS, LEARNING AND ROBOTIC KITS, PCB BOARD
Have any Questions?
Feel free to Get in touch
Guarantee Safe and Secure Payment Checkout
Description
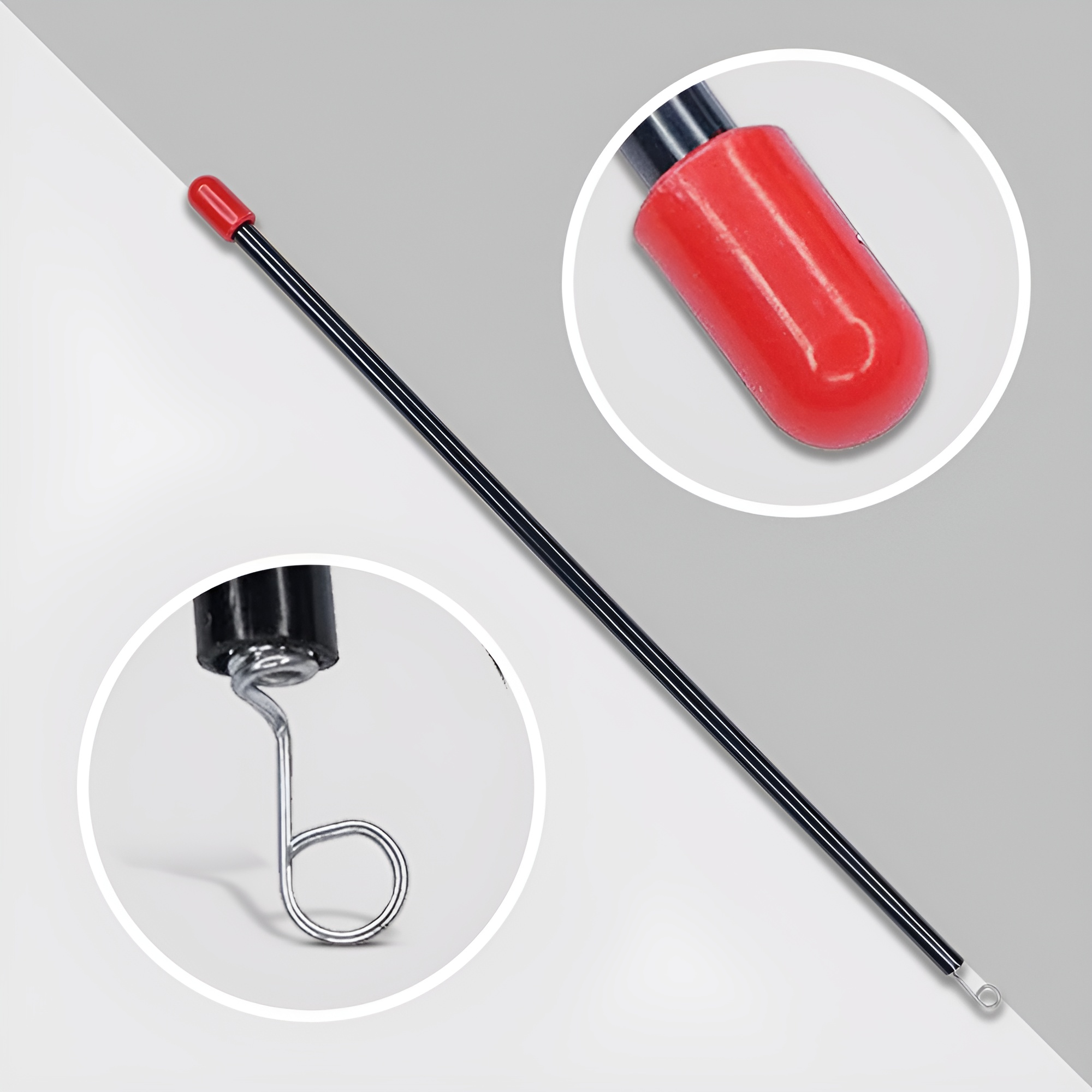
The 4 Channel RC Transmitter and Receiver set is a versatile and reliable wireless control system designed for remote-controlled applications. Ideal for hobbyists, model enthusiasts, and robotics projects, this set enables precise control of various devices, including drones, cars, and boats.
Transmitter:
- Channels: A 4-channel transmitter can control four different functions. For example, in a drone, this might include throttle, yaw, pitch, and roll.
- Control Types: Typically features joysticks, switches, and knobs for precise control.
- Frequency: Operates on specific frequencies (like 2.4GHz) to minimize interference.
- Battery: Usually powered by rechargeable batteries or AA batteries.
Receiver:
- Channels: The receiver must match the transmitter in the number of channels.
- Connection: Receives signals from the transmitter and sends them to the servos or electronic speed controllers (ESC) in the model.
- Range: Effective range varies but is generally several hundred meters.
Important Points
- Compatibility: Ensure that the transmitter and receiver are compatible, particularly in frequency and modulation type (e.g., PWM, PPM, or digital).
- Binding: Most systems require a binding process to link the transmitter and receiver, ensuring that they communicate with each other.
- Failsafe Features: Look for receivers with failsafe settings that can automatically return the vehicle to a safe state if the signal is lost.
- Channel Mapping: Understand how channels are mapped to specific functions to avoid confusion during operation.
- Interference: 2.4GHz systems generally provide better resistance to interference compared to older 27MHz or 72MHz systems.
- Range Limitations: Be aware of the effective range of your transmitter and receiver to prevent loss of control.
- Maintenance: Regularly check the transmitter and receiver for battery levels and ensure connections are secure to maintain performance.
- Legal Regulations: Be mindful of local regulations regarding the use of RC devices, especially concerning frequencies and permitted power levels.
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.
Related products
Sale!
10k, Vertical P...
Sale!
PIC16F1503-I/SL...
Sale!
Gy-521 Mpu-6050...
Sale!
Quickfix Solder...
Sale!
Hc-05 Bluetooth...
Need help? Call us:
+91 9899799757












Reviews
There are no reviews yet.